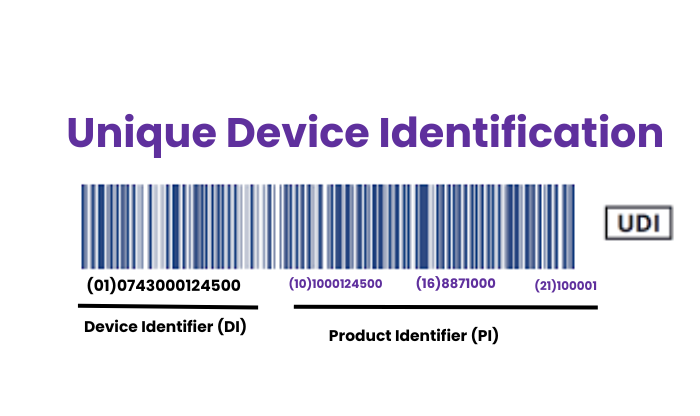
- Definition : The UDI is a series of numeric or alphanumeric characters that provides a globally unique identifier for medical devices within the EU market. It is designed to facilitate easier tracking and identification of devices throughout their supply chain and use.
- Components: The UDI typically consists of:
- UDI-DI (Device Identifier): A static code that identifies the device and its manufacturer.
- UDI-PI (Production Identifier): A dynamic code that contains the production information of the device, such as batch number, serial number, manufacturing, and expiration dates.
Purpose and Benefits
- Improved Traceability : Enhances the ability to trace devices through the healthcare supply chain.
- Enhanced Patient Safety : Facilitates rapid and precise recalls and improves adverse event reporting.
- Increased Transparency : Provides a standardized identifier to support global harmonization.
UDI Issuing Entities in the EU
- Designated Entities : The European Commission designates entities responsible for issuing UDIs. Entities like GS1, HIBCC, and ICCBBA are recognized for this purpose.
- Manufacturer’s Role : Manufacturers must obtain UDIs from these entities and ensure compliance with the specific standards and formats they provide.
Obtaining and Implementing UDI in the EU
- Select an Issuing Entity : Manufacturers should choose an entity recognized by the European Commission.
- Generate the UDI : Follow the guidelines provided by the issuing entity to create both the UDI-DI and UDI-PI.
- Label and Package : Apply the UDI on the device’s label and all higher levels of packaging. For certain device categories, direct marking on the device is also required.
- Data Submission : Submit the UDI data to EUDAMED (European Database on Medical Devices), which is the central repository for information on medical devices placed on the market in the EU.
Compliance with EU MDR and EU IVDR
- Regulatory Framework : The UDI system is a fundamental part of the regulatory framework established by the EU MDR and IVDR.
- Timelines and Transition : The EU has set specific deadlines for compliance with UDI requirements, which vary depending on the device classification.
- Integration with EUDAMED : The UDI system in the EU is closely integrated with EUDAMED, which serves as the central database for device registration and surveillance.
Key Considerations for Manufacturers
- Adherence to Standards : Ensuring that UDIs are generated and applied in accordance with the standards set by the designated issuing entities.
- Data Management : Managing and maintaining UDI data requires robust systems, especially for manufacturers with diverse and extensive product lines.
- Global Considerations : For manufacturers operating globally, understanding the nuances between the EU’s UDI system and other international systems is crucial.
MDCG Guidance Documents :
- Q&A on the Unique Device Identification system under Regulation (EU) 2017/745 and Regulation (EU)
- Guidance on UDI for systems and procedure packs
- UDI assignment to medical device software
- Clarifications of UDI related responsibilities in relation to article 16
- MDCG guiding principles for issuing entities rules on basic UDI-DI
Conclusion
In the European Union, the UDI system represents a significant advancement in the regulatory landscape for medical devices. It’s aimed at enhancing patient safety, improving the effectiveness of device recalls, and facilitating better post-market surveillance. For manufacturers, compliance with the UDI requirements under the EU MDR and IVDR is essential. This involves not only the generation and application of the UDI but also the integration of this information into the broader regulatory framework, including the submission of data to EUDAMED. As the medical device industry continues to evolve, the UDI system will play a vital role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of medical devices across Europe.